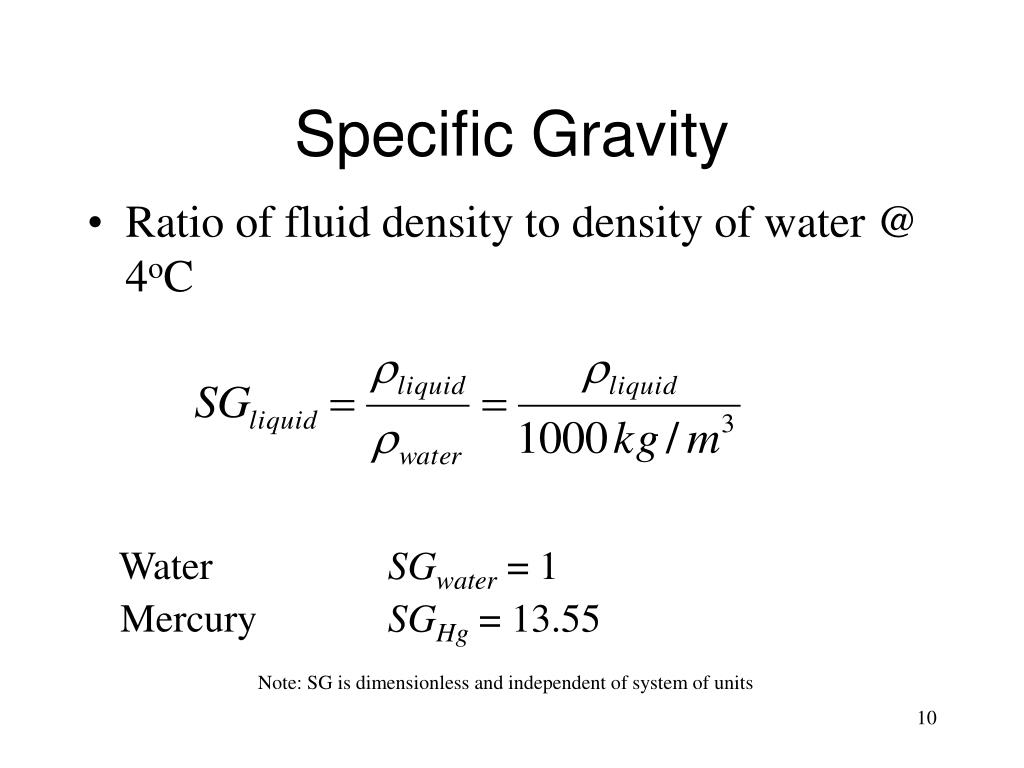
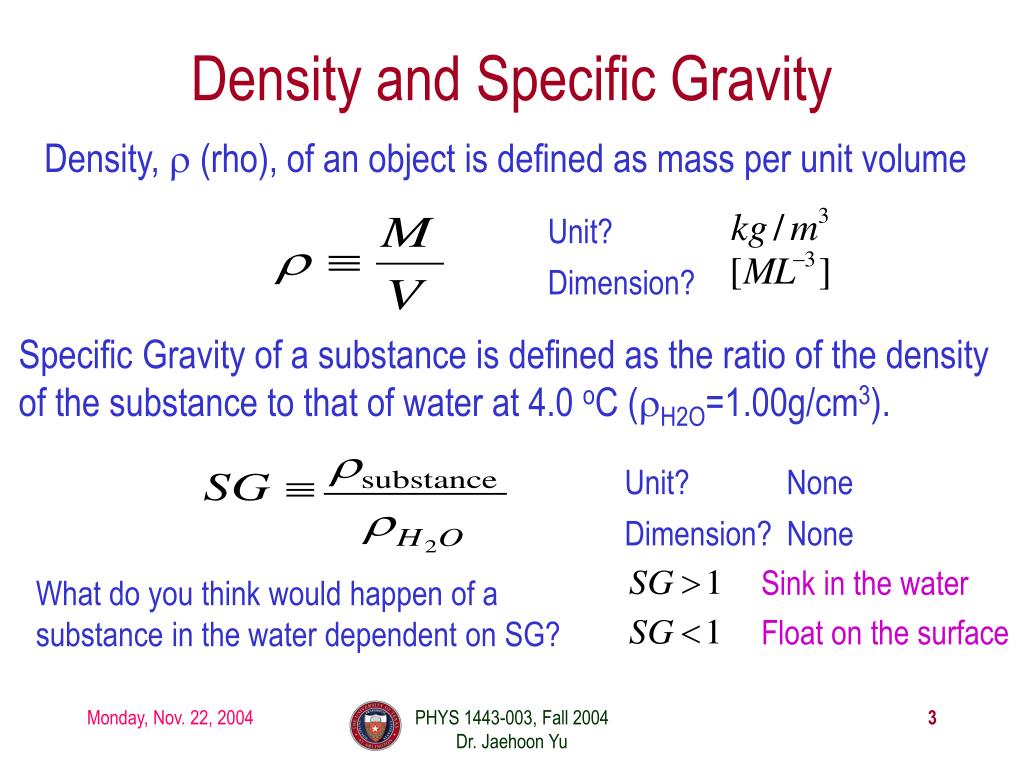
Specific Gravity Formula
Specific Gravity Formula - Specific gravity is determined by dividing the density of a material by the density of water at 4 degrees celsius. For the calculation, the density of the material and that of the water must be. Specific gravity, ratio of the density of a substance to that of a standard substance. The specific gravity formula is defined as the ratio of the density of an object to the density of water, with water as the reference substance. Calculate the ratio between the densities: Use a scale to measure the mass of that volume: Also, the greek symbol rho \(\rho\). The usual standard of comparison for solids and liquids is water at 4 °c (39.2 °f), which has a. The specific gravity formula is defined with, water as its reference substance and the formula is the ratio of the density of an object to the density of the water. To calculate the specific gravity of a substance, follow these easy steps:
To calculate the specific gravity of a substance, follow these easy steps: Specific gravity is determined by dividing the density of a material by the density of water at 4 degrees celsius. Also, the greek symbol rho \(\rho\). The specific gravity formula is defined with, water as its reference substance and the formula is the ratio of the density of an object to the density of the water. Use a scale to measure the mass of that volume: The specific gravity formula is defined as the ratio of the density of an object to the density of water, with water as the reference substance. For the calculation, the density of the material and that of the water must be. The usual standard of comparison for solids and liquids is water at 4 °c (39.2 °f), which has a. Calculate the ratio between the densities: Specific gravity, ratio of the density of a substance to that of a standard substance.
The specific gravity formula is defined as the ratio of the density of an object to the density of water, with water as the reference substance. Also, the greek symbol rho \(\rho\). Specific gravity, ratio of the density of a substance to that of a standard substance. Use a scale to measure the mass of that volume: For the calculation, the density of the material and that of the water must be. Specific gravity is determined by dividing the density of a material by the density of water at 4 degrees celsius. To calculate the specific gravity of a substance, follow these easy steps: Calculate the ratio between the densities: The usual standard of comparison for solids and liquids is water at 4 °c (39.2 °f), which has a. The specific gravity formula is defined with, water as its reference substance and the formula is the ratio of the density of an object to the density of the water.
PPT SPECIFIC GRAVITY & ABSORPTION CAPACITY OF AGGREGATES PowerPoint
Specific gravity, ratio of the density of a substance to that of a standard substance. Specific gravity is determined by dividing the density of a material by the density of water at 4 degrees celsius. Also, the greek symbol rho \(\rho\). Use a scale to measure the mass of that volume: To calculate the specific gravity of a substance, follow.
Getting Started (process variables specific gravity/formulas) YouTube
The specific gravity formula is defined with, water as its reference substance and the formula is the ratio of the density of an object to the density of the water. Specific gravity, ratio of the density of a substance to that of a standard substance. Use a scale to measure the mass of that volume: Calculate the ratio between the.
Specific Gravity Formula Definition, Equations, Examples
The usual standard of comparison for solids and liquids is water at 4 °c (39.2 °f), which has a. The specific gravity formula is defined with, water as its reference substance and the formula is the ratio of the density of an object to the density of the water. Also, the greek symbol rho \(\rho\). Calculate the ratio between the.
Specific Gravity of Cement by Specific Gravity Bottle Learning Technology
Specific gravity, ratio of the density of a substance to that of a standard substance. Specific gravity is determined by dividing the density of a material by the density of water at 4 degrees celsius. To calculate the specific gravity of a substance, follow these easy steps: Use a scale to measure the mass of that volume: The specific gravity.
PPT FLUID PROPERTIES Chapter 2 PowerPoint Presentation, free download
To calculate the specific gravity of a substance, follow these easy steps: Specific gravity, ratio of the density of a substance to that of a standard substance. For the calculation, the density of the material and that of the water must be. Specific gravity is determined by dividing the density of a material by the density of water at 4.
PPT Density and Specific Gravity Fluid and Pressure Absolute and
The specific gravity formula is defined with, water as its reference substance and the formula is the ratio of the density of an object to the density of the water. Specific gravity, ratio of the density of a substance to that of a standard substance. The usual standard of comparison for solids and liquids is water at 4 °c (39.2.
Specific Gravity YouTube
Specific gravity is determined by dividing the density of a material by the density of water at 4 degrees celsius. Calculate the ratio between the densities: Specific gravity, ratio of the density of a substance to that of a standard substance. To calculate the specific gravity of a substance, follow these easy steps: The specific gravity formula is defined with,.
PPT Specific Gravity of Soils PowerPoint Presentation ID270222
The specific gravity formula is defined with, water as its reference substance and the formula is the ratio of the density of an object to the density of the water. Specific gravity is determined by dividing the density of a material by the density of water at 4 degrees celsius. For the calculation, the density of the material and that.
Determination of Specific Gravity of solids using pycnometer YouTube
Specific gravity is determined by dividing the density of a material by the density of water at 4 degrees celsius. The specific gravity formula is defined with, water as its reference substance and the formula is the ratio of the density of an object to the density of the water. The usual standard of comparison for solids and liquids is.
Solved The specific gravity of an object with density
Specific gravity, ratio of the density of a substance to that of a standard substance. Calculate the ratio between the densities: The specific gravity formula is defined as the ratio of the density of an object to the density of water, with water as the reference substance. The specific gravity formula is defined with, water as its reference substance and.
Also, The Greek Symbol Rho \(\Rho\).
The specific gravity formula is defined with, water as its reference substance and the formula is the ratio of the density of an object to the density of the water. Specific gravity is determined by dividing the density of a material by the density of water at 4 degrees celsius. To calculate the specific gravity of a substance, follow these easy steps: Specific gravity, ratio of the density of a substance to that of a standard substance.
The Specific Gravity Formula Is Defined As The Ratio Of The Density Of An Object To The Density Of Water, With Water As The Reference Substance.
Calculate the ratio between the densities: Use a scale to measure the mass of that volume: For the calculation, the density of the material and that of the water must be. The usual standard of comparison for solids and liquids is water at 4 °c (39.2 °f), which has a.