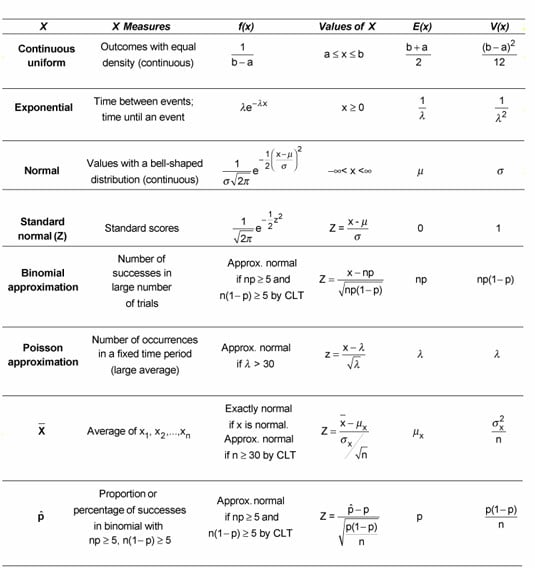
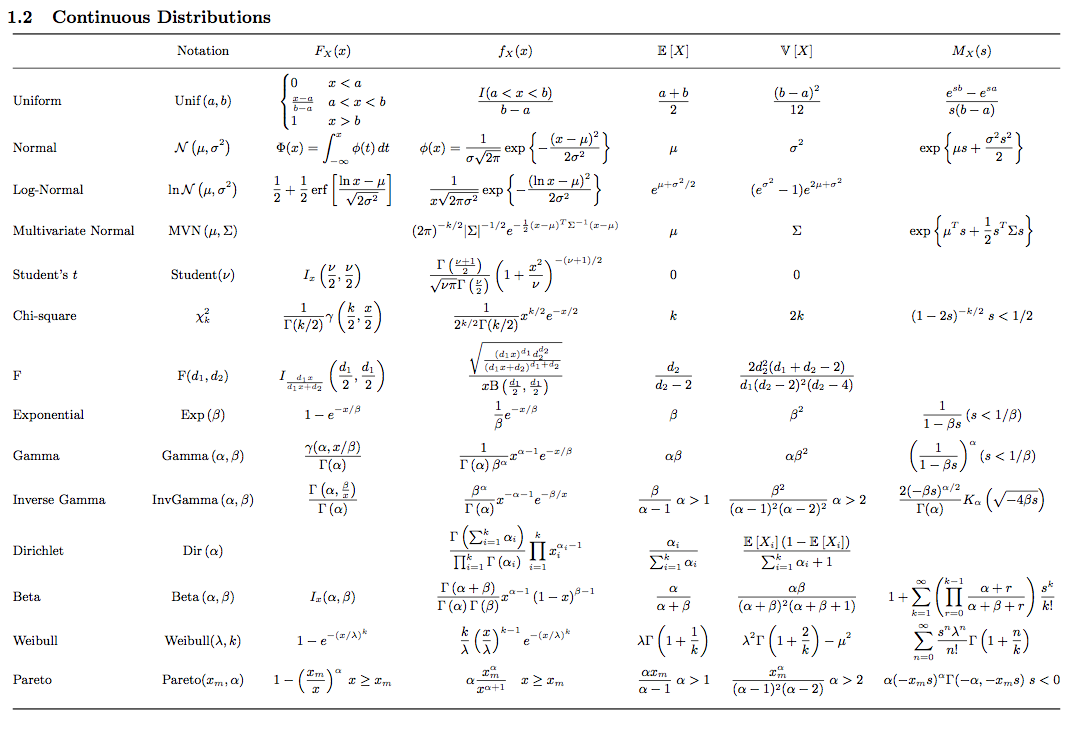
Probability Distribution Cheat Sheet
Probability Distribution Cheat Sheet - Probability cheat sheet • p(ac) = 1−p(a) • p(a∪b) = p(a)+p(b) if a,b do not overlap. Distributions probability mass function (pmf) (discrete only) is a function that takes in the value x, and gives the probability that. A random variable x with a discrete uniform distribution with parameters a and b can take each of the integers a, a+1., b with equal probability. • p(a∩b) = p(a)p(b) if a,b are independent. 1) the binomial distribution converges to the poisson distribution when n is large, p is small and np<10. • e(ax +by +c) = aex +bey.
Probability cheat sheet • p(ac) = 1−p(a) • p(a∪b) = p(a)+p(b) if a,b do not overlap. • e(ax +by +c) = aex +bey. • p(a∩b) = p(a)p(b) if a,b are independent. Distributions probability mass function (pmf) (discrete only) is a function that takes in the value x, and gives the probability that. A random variable x with a discrete uniform distribution with parameters a and b can take each of the integers a, a+1., b with equal probability. 1) the binomial distribution converges to the poisson distribution when n is large, p is small and np<10.
Probability cheat sheet • p(ac) = 1−p(a) • p(a∪b) = p(a)+p(b) if a,b do not overlap. • p(a∩b) = p(a)p(b) if a,b are independent. • e(ax +by +c) = aex +bey. A random variable x with a discrete uniform distribution with parameters a and b can take each of the integers a, a+1., b with equal probability. Distributions probability mass function (pmf) (discrete only) is a function that takes in the value x, and gives the probability that. 1) the binomial distribution converges to the poisson distribution when n is large, p is small and np<10.
Probability For Dummies Cheat Sheet dummies
Distributions probability mass function (pmf) (discrete only) is a function that takes in the value x, and gives the probability that. A random variable x with a discrete uniform distribution with parameters a and b can take each of the integers a, a+1., b with equal probability. • e(ax +by +c) = aex +bey. 1) the binomial distribution converges to.
Probability Rules Cheat Sheet. Basic probability rules with examples
1) the binomial distribution converges to the poisson distribution when n is large, p is small and np<10. • e(ax +by +c) = aex +bey. Probability cheat sheet • p(ac) = 1−p(a) • p(a∪b) = p(a)+p(b) if a,b do not overlap. Distributions probability mass function (pmf) (discrete only) is a function that takes in the value x, and gives the.
SOLUTION Probability distribution cheat sheet Studypool
1) the binomial distribution converges to the poisson distribution when n is large, p is small and np<10. • e(ax +by +c) = aex +bey. Probability cheat sheet • p(ac) = 1−p(a) • p(a∪b) = p(a)+p(b) if a,b do not overlap. A random variable x with a discrete uniform distribution with parameters a and b can take each of the.
This cheat sheet covers the basics of a calculusbased probability and
A random variable x with a discrete uniform distribution with parameters a and b can take each of the integers a, a+1., b with equal probability. • p(a∩b) = p(a)p(b) if a,b are independent. Probability cheat sheet • p(ac) = 1−p(a) • p(a∪b) = p(a)+p(b) if a,b do not overlap. • e(ax +by +c) = aex +bey. 1) the binomial.
Matthias Vallentin Probability and Statistics Cheat Sheet
A random variable x with a discrete uniform distribution with parameters a and b can take each of the integers a, a+1., b with equal probability. 1) the binomial distribution converges to the poisson distribution when n is large, p is small and np<10. • p(a∩b) = p(a)p(b) if a,b are independent. • e(ax +by +c) = aex +bey. Probability.
SOLUTION Probability distribution cheat sheet Studypool
• e(ax +by +c) = aex +bey. Distributions probability mass function (pmf) (discrete only) is a function that takes in the value x, and gives the probability that. • p(a∩b) = p(a)p(b) if a,b are independent. A random variable x with a discrete uniform distribution with parameters a and b can take each of the integers a, a+1., b with.
Probability Cheat Sheet Probability Distribution Covariance Matrix
1) the binomial distribution converges to the poisson distribution when n is large, p is small and np<10. Distributions probability mass function (pmf) (discrete only) is a function that takes in the value x, and gives the probability that. A random variable x with a discrete uniform distribution with parameters a and b can take each of the integers a,.
Probability Cheatsheet Covariance Normal Distribution
Probability cheat sheet • p(ac) = 1−p(a) • p(a∪b) = p(a)+p(b) if a,b do not overlap. Distributions probability mass function (pmf) (discrete only) is a function that takes in the value x, and gives the probability that. A random variable x with a discrete uniform distribution with parameters a and b can take each of the integers a, a+1., b.
SOLUTION Probability distribution cheat sheet Studypool
1) the binomial distribution converges to the poisson distribution when n is large, p is small and np<10. Probability cheat sheet • p(ac) = 1−p(a) • p(a∪b) = p(a)+p(b) if a,b do not overlap. • e(ax +by +c) = aex +bey. • p(a∩b) = p(a)p(b) if a,b are independent. Distributions probability mass function (pmf) (discrete only) is a function that.
The Ultimate Probability Cheatsheet Probability Theory Covariance
• p(a∩b) = p(a)p(b) if a,b are independent. Distributions probability mass function (pmf) (discrete only) is a function that takes in the value x, and gives the probability that. Probability cheat sheet • p(ac) = 1−p(a) • p(a∪b) = p(a)+p(b) if a,b do not overlap. • e(ax +by +c) = aex +bey. 1) the binomial distribution converges to the poisson.
Distributions Probability Mass Function (Pmf) (Discrete Only) Is A Function That Takes In The Value X, And Gives The Probability That.
1) the binomial distribution converges to the poisson distribution when n is large, p is small and np<10. • e(ax +by +c) = aex +bey. A random variable x with a discrete uniform distribution with parameters a and b can take each of the integers a, a+1., b with equal probability. Probability cheat sheet • p(ac) = 1−p(a) • p(a∪b) = p(a)+p(b) if a,b do not overlap.