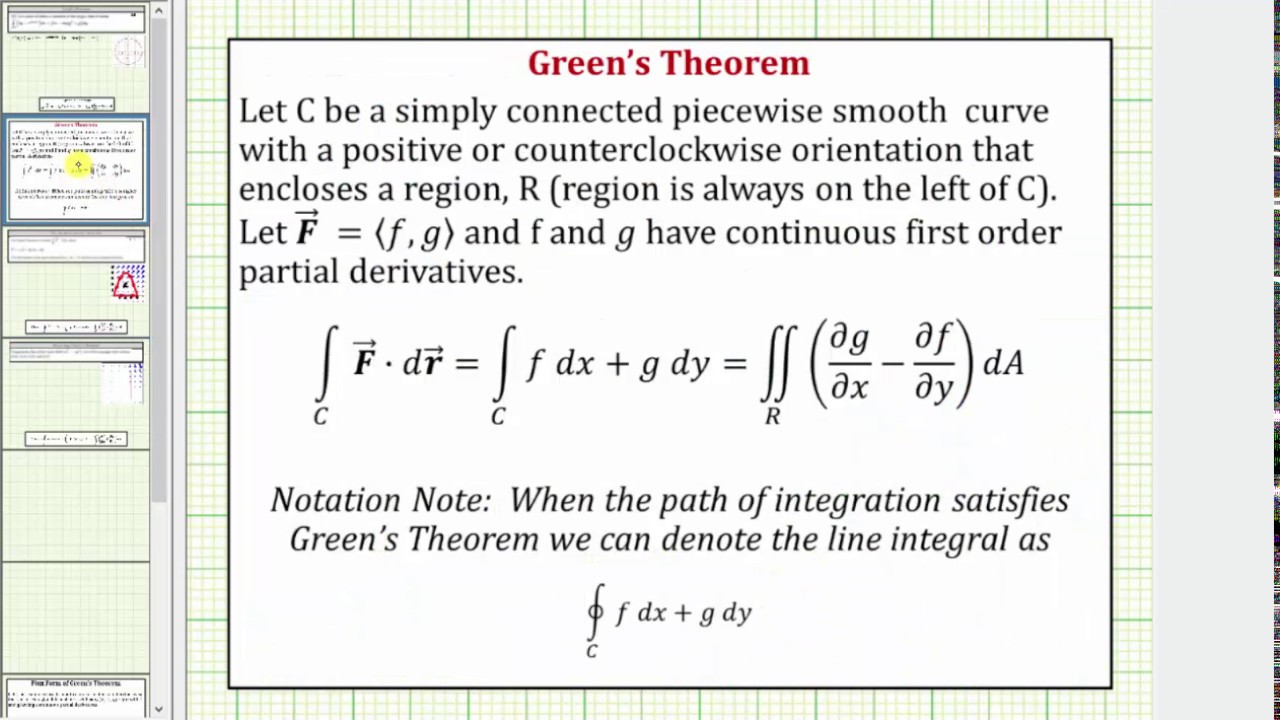
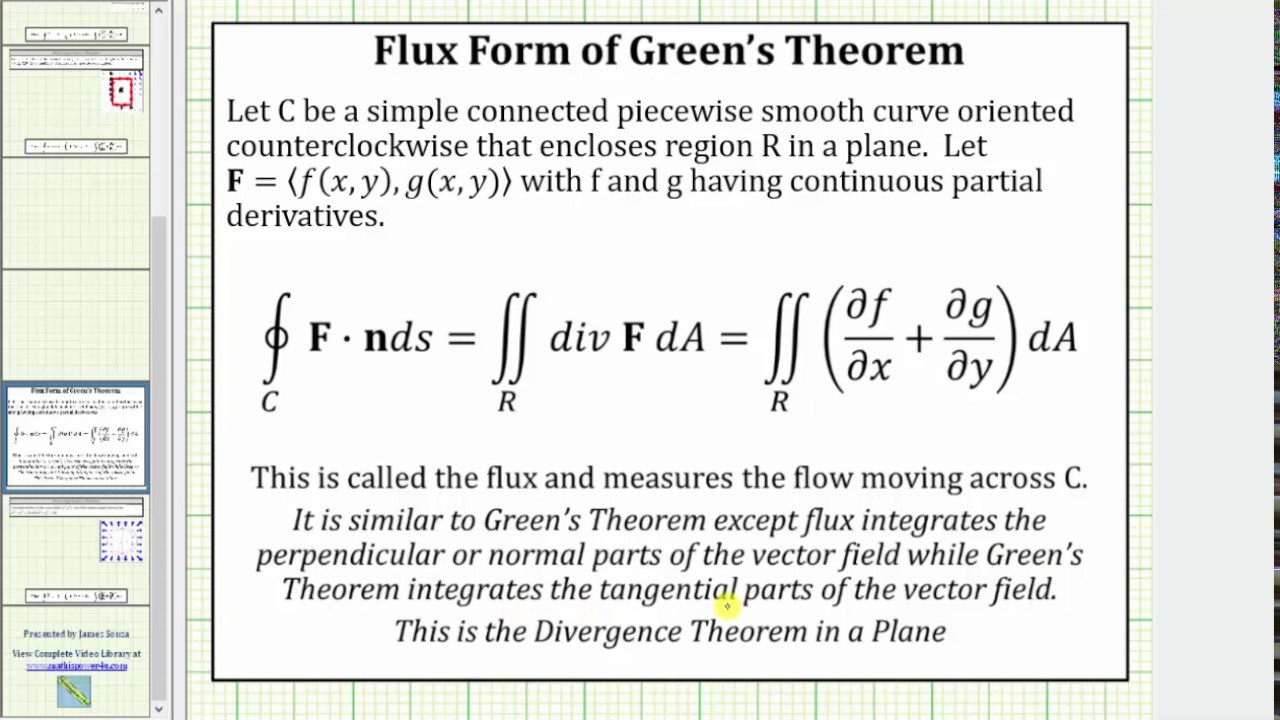
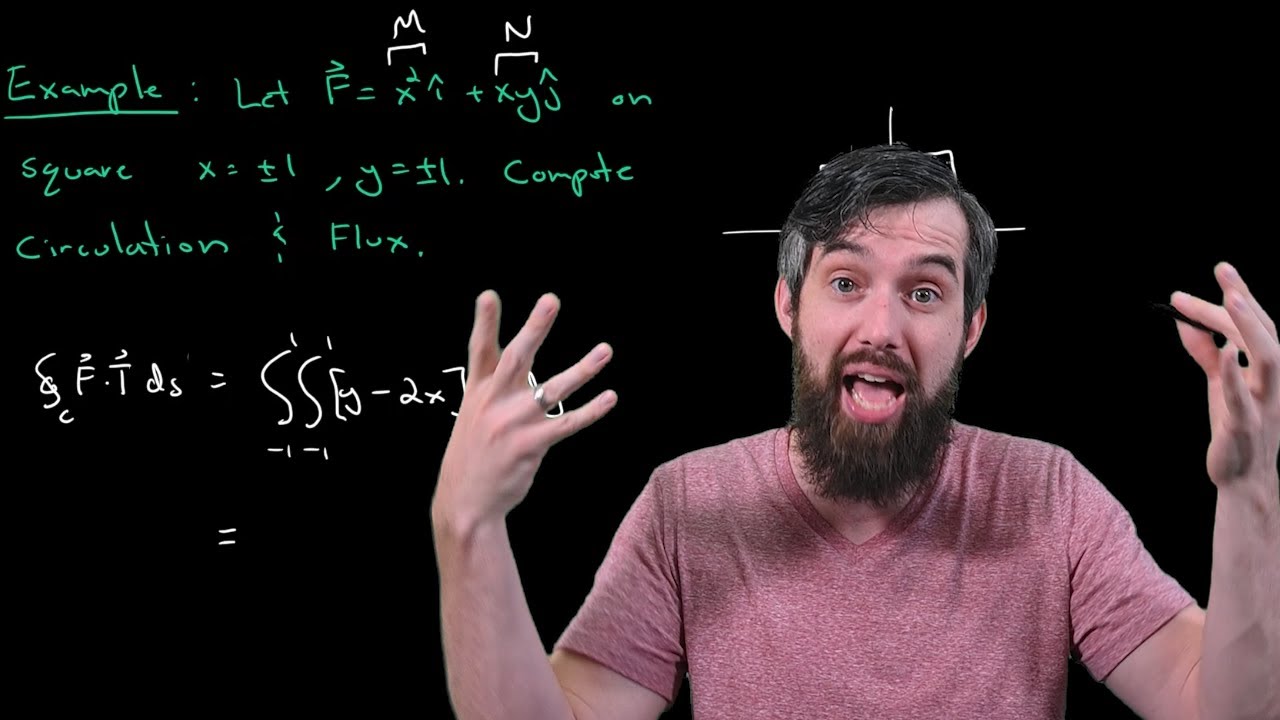Flux Form Of Green S Theorem
Flux Form Of Green S Theorem - The integral we would normally use to calculate the area is just \iint_r 1\,da ∬ r1da. We substitute l(f) in place of f in equation (2) and use the. The flux form of green’s theorem relates a double integral over region \(d\) to the flux across boundary \(c\). The flux of a fluid. Green's theorem can be used to find the area of a 2d shape. The flux form of green’s theorem relates a double integral over region [latex]d[/latex] to the flux across curve [latex]c[/latex]. In a similar way, the flux form of green’s theorem follows from the circulation form:
The flux of a fluid. Green's theorem can be used to find the area of a 2d shape. In a similar way, the flux form of green’s theorem follows from the circulation form: The flux form of green’s theorem relates a double integral over region \(d\) to the flux across boundary \(c\). The flux form of green’s theorem relates a double integral over region [latex]d[/latex] to the flux across curve [latex]c[/latex]. We substitute l(f) in place of f in equation (2) and use the. The integral we would normally use to calculate the area is just \iint_r 1\,da ∬ r1da.
In a similar way, the flux form of green’s theorem follows from the circulation form: The flux form of green’s theorem relates a double integral over region \(d\) to the flux across boundary \(c\). The integral we would normally use to calculate the area is just \iint_r 1\,da ∬ r1da. We substitute l(f) in place of f in equation (2) and use the. Green's theorem can be used to find the area of a 2d shape. The flux form of green’s theorem relates a double integral over region [latex]d[/latex] to the flux across curve [latex]c[/latex]. The flux of a fluid.
Green's Theorem Flux Form YouTube
The flux form of green’s theorem relates a double integral over region [latex]d[/latex] to the flux across curve [latex]c[/latex]. The flux form of green’s theorem relates a double integral over region \(d\) to the flux across boundary \(c\). The integral we would normally use to calculate the area is just \iint_r 1\,da ∬ r1da. We substitute l(f) in place of.
Determine the Flux of a 2D Vector Field Using Green's Theorem (Parabola
The flux form of green’s theorem relates a double integral over region [latex]d[/latex] to the flux across curve [latex]c[/latex]. The flux of a fluid. In a similar way, the flux form of green’s theorem follows from the circulation form: The integral we would normally use to calculate the area is just \iint_r 1\,da ∬ r1da. We substitute l(f) in place.
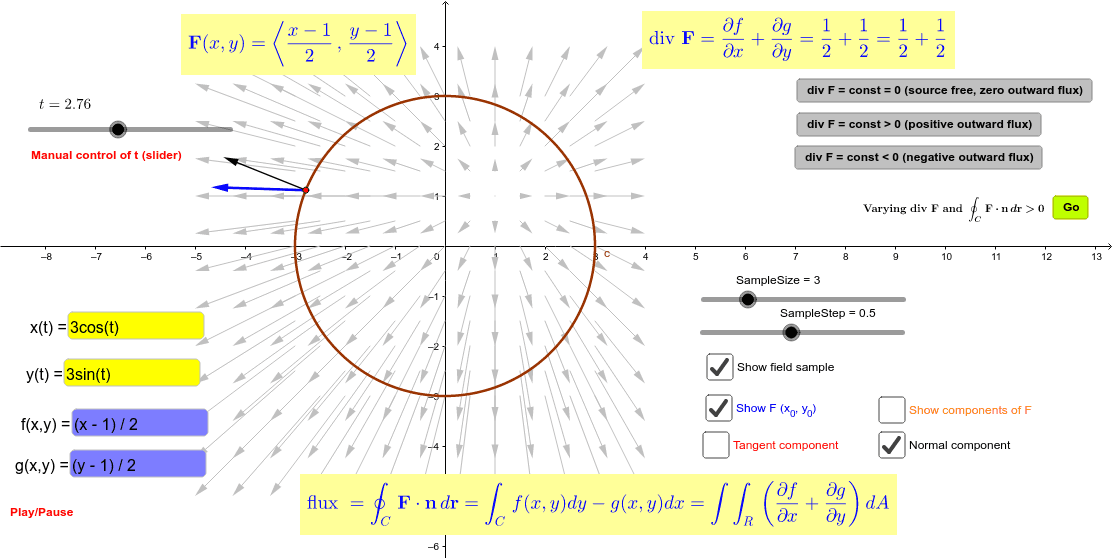
Illustration of the flux form of the Green's Theorem GeoGebra
The integral we would normally use to calculate the area is just \iint_r 1\,da ∬ r1da. In a similar way, the flux form of green’s theorem follows from the circulation form: The flux form of green’s theorem relates a double integral over region \(d\) to the flux across boundary \(c\). The flux form of green’s theorem relates a double integral.
Multivariable Calculus Green's Theorem YouTube
In a similar way, the flux form of green’s theorem follows from the circulation form: Green's theorem can be used to find the area of a 2d shape. The flux of a fluid. The integral we would normally use to calculate the area is just \iint_r 1\,da ∬ r1da. We substitute l(f) in place of f in equation (2) and.
Flux Form of Green's Theorem YouTube
Green's theorem can be used to find the area of a 2d shape. The flux form of green’s theorem relates a double integral over region [latex]d[/latex] to the flux across curve [latex]c[/latex]. In a similar way, the flux form of green’s theorem follows from the circulation form: The flux form of green’s theorem relates a double integral over region \(d\).
Example Using Green's Theorem to Compute Circulation & Flux // Vector
The flux form of green’s theorem relates a double integral over region [latex]d[/latex] to the flux across curve [latex]c[/latex]. The flux of a fluid. The integral we would normally use to calculate the area is just \iint_r 1\,da ∬ r1da. We substitute l(f) in place of f in equation (2) and use the. Green's theorem can be used to find.
Determine the Flux of a 2D Vector Field Using Green's Theorem
The integral we would normally use to calculate the area is just \iint_r 1\,da ∬ r1da. The flux of a fluid. We substitute l(f) in place of f in equation (2) and use the. The flux form of green’s theorem relates a double integral over region \(d\) to the flux across boundary \(c\). Green's theorem can be used to find.
Determine the Flux of a 2D Vector Field Using Green's Theorem (Hole
The integral we would normally use to calculate the area is just \iint_r 1\,da ∬ r1da. The flux form of green’s theorem relates a double integral over region \(d\) to the flux across boundary \(c\). The flux form of green’s theorem relates a double integral over region [latex]d[/latex] to the flux across curve [latex]c[/latex]. Green's theorem can be used to.
Flux Form of Green's Theorem Vector Calculus YouTube
We substitute l(f) in place of f in equation (2) and use the. The flux of a fluid. The flux form of green’s theorem relates a double integral over region \(d\) to the flux across boundary \(c\). In a similar way, the flux form of green’s theorem follows from the circulation form: The integral we would normally use to calculate.
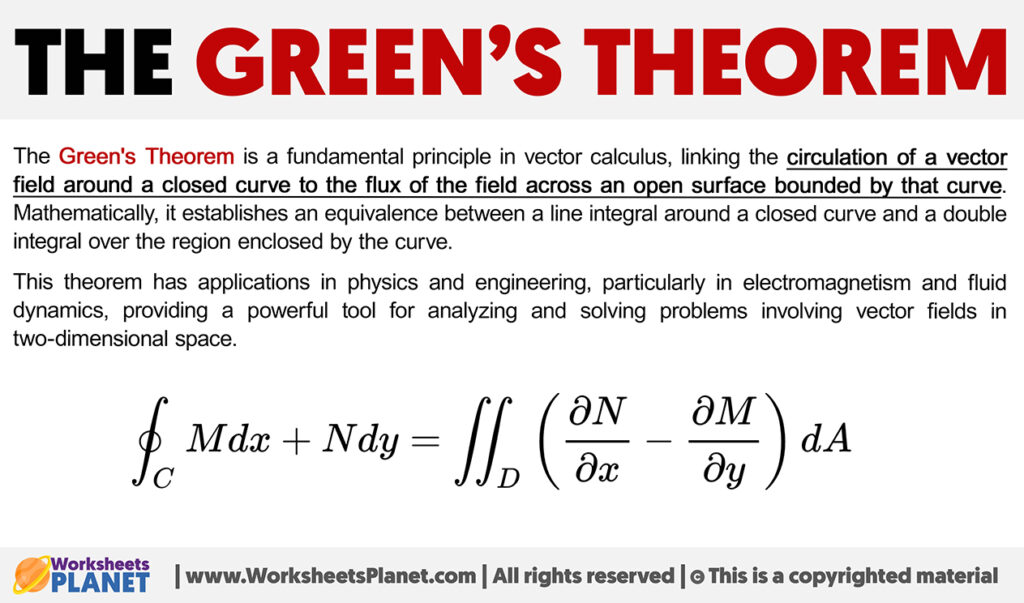
The Green's Theorem Formula + Definition
Green's theorem can be used to find the area of a 2d shape. The integral we would normally use to calculate the area is just \iint_r 1\,da ∬ r1da. The flux form of green’s theorem relates a double integral over region [latex]d[/latex] to the flux across curve [latex]c[/latex]. The flux of a fluid. We substitute l(f) in place of f.
In A Similar Way, The Flux Form Of Green’s Theorem Follows From The Circulation Form:
Green's theorem can be used to find the area of a 2d shape. The integral we would normally use to calculate the area is just \iint_r 1\,da ∬ r1da. The flux form of green’s theorem relates a double integral over region \(d\) to the flux across boundary \(c\). The flux of a fluid.
We Substitute L(F) In Place Of F In Equation (2) And Use The.
The flux form of green’s theorem relates a double integral over region [latex]d[/latex] to the flux across curve [latex]c[/latex].